Electric bicycles (e-bikes) have revolutionized personal transportation, providing an eco-friendly and convenient alternative to traditional bicycles and motor vehicles. However, as their popularity grows, so does the need for clear regulations to ensure safety and proper use. If you're an e-bike rider in California, it's essential to understand the laws that govern different classes of electric bicycles and how they affect your riding experience.
What is an Electric Bicycle?
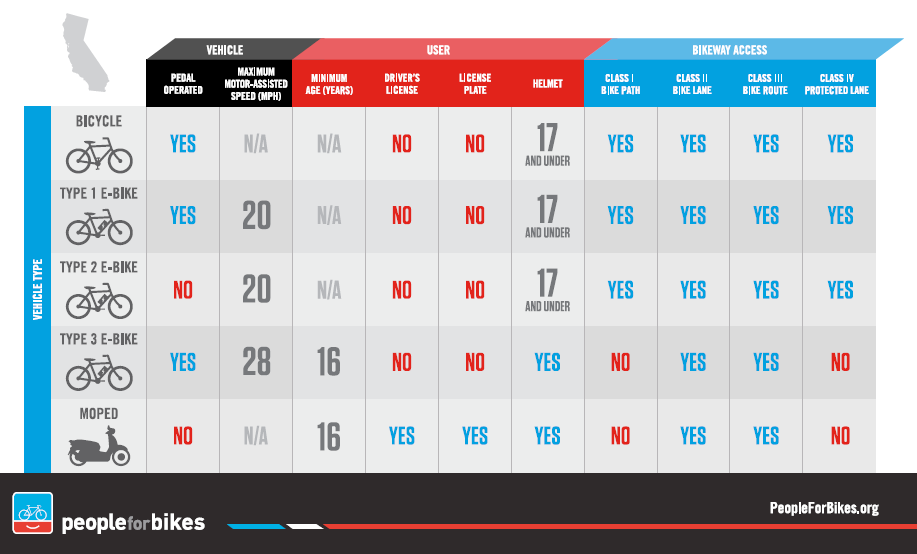
An electric bicycle is defined as a bicycle equipped with fully operable pedals and an electric motor of less than 750 watts. This means e-bikes are distinct from motorcycles or mopeds, which require special licensing and registration. To ensure safe use, California has categorized e-bikes into three distinct classes:
Class 1: Pedal-Assist E-Bikes
Class 1 electric bicycles are equipped with a motor that provides assistance only when the rider is pedaling. Once the bike reaches a speed of 20 mph, the motor ceases to assist. These bikes are often favored for city commuting and recreational riding because they closely mimic the traditional cycling experience while offering an extra boost.
Class 2: Throttle-Assisted E-Bikes
Unlike Class 1 e-bikes, Class 2 models have a throttle that can propel the bike without the need for pedaling. However, they are still limited to a maximum assisted speed of 20 mph. These e-bikes are popular among riders who want motor assistance without having to pedal constantly.
Class 3: High-Speed Pedal-Assist E-Bikes
Class 3 electric bicycles are similar to Class 1 but come with a speedometer and can provide assistance up to 28 mph while the rider is pedaling. Due to their higher speeds, additional safety regulations apply to Class 3 e-bikes.
Rules for Class 3 E-Bike Riders
To ensure the safety of riders and others on the road, California has specific laws governing the operation of Class 3 e-bikes:
-
Riders must be at least 16 years old.
-
A bicycle helmet is mandatory.
-
Passengers are not allowed.
-
Riding in a bicycle lane is permitted only if authorized by local authorities.
Are E-Bikes Subject to Licensing and Registration?
One of the advantages of e-bikes in California is that they are exempt from motor vehicle financial responsibility laws. This means:
-
No driver’s license is required.
-
No registration or license plate is necessary.
-
No insurance is needed.
This makes e-bikes an accessible and cost-effective transportation option compared to cars and motorcycles.
Where Can You Ride an E-Bike in California?
E-bike accessibility varies by class and local regulations:
-
Class 1 and Class 2 e-bikes are generally allowed on bike paths, lanes, and multi-use trails unless local laws state otherwise.
-
Class 3 e-bikes are typically restricted from multi-use paths but can be used in bike lanes on streets.
Local municipalities have the authority to enforce additional restrictions, so always check local ordinances before riding.
Final Thoughts
As e-bikes continue to grow in popularity, understanding the laws governing their use is crucial for both safety and compliance. Whether you're commuting, exploring trails, or simply enjoying a ride, knowing the distinctions between Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3 e-bikes will help you stay within legal limits and ensure a smooth riding experience.
By following these regulations, riders can enjoy the benefits of electric bicycles while promoting road safety for everyone. If you're considering purchasing an e-bike, be sure to choose one that aligns with your intended use and local riding laws.
(Credits to PeopleforBikes.org for the table image above about the e-bike types.)